

#0.05 UF CAPACITOR CODE CHART FULL#
The second diagram shows a full charge and no current flowing after a period of 5 RC time constants. Current just starts flowing with 0 volts across the capacitor and it has a balanced charge. In this diagram, the first circuit shows the moment the circuit is closed. Using the properties of charge time, we can determine that a capacitor will have more than 99% of its charge after 5 time constants, or 5 * RC seconds. As an example, if the resistor is 20k Ohms and the capacitor is 200 pF (picofarads), the RC time constant is:Ģ0000 ohms * 2e-10 farads = 4 microseconds The result is a time value called the RC time constant. A simple circuit to charge a capacitor is shown in the following diagram.Ī special value for a capacitor charging circuit is found by multiplying the amount of resistance to it by the capacitance. Once the capacitor is fully charged, current will stop flowing to it because there’s no more room to accept any new charges. For any amount of voltage across the plates of a capacitor it will take some time until it becomes fully charged. It takes time to charge due to some resistance to the current flowing to or from its plates. In reality, a capacitor doesn’t charge immediately. Charges relocate and move to the plate in the direction of their attraction. The illustration below shows a capacitor with two plates that are oppositely charged by a force of the voltage applied to them. This happens until the capacitor plates are full of opposing charges. The presence of an electric field between these surfaces forces the charges on the plates to locate themselves closest to the direction of opposite charge. Inside the gap, however, is an electric field ( E) which directs the force from the battery to push an opposite electric charge to the plates.

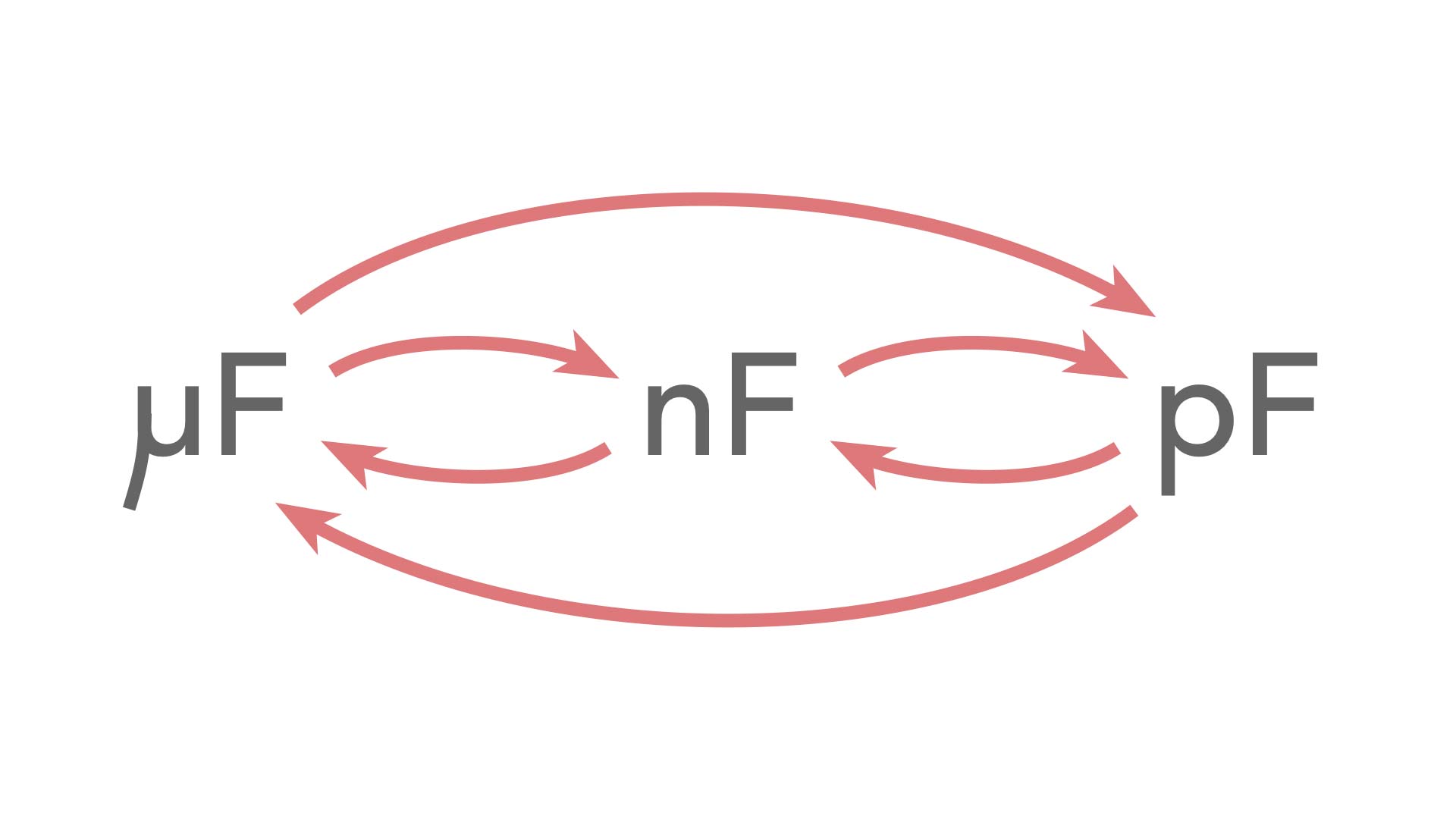
The gap could be air or some other non-conductive material. The charges can’t pass to the other plate due to the gap between them that insulates the plates from each other. Electric fieldĪt first, a capacitor has an equal amount of both positive and negative charge on each plate. A picofarad is really small, it’s 1 / 1000000000000 of a Farad. Most of the capacitors used in small, modern electronic circuits are in the microfarad (uF) or picofarad (pF) range. The amount of capacitance ( C) a capacitor has depends on the ability of the electric field to influence the charges on its plates, times the area of the conductive surface, divided by the distance between the plates.Ĭapacitance is measured in units of Farads (F). Here’s an illustration of how the parts of a capacitor go together along with their important properties: What matters is the area of the plates ( A) and the distance between them ( d). This along with the dimensions of the capacitor plates determine how much charge it can store. The ability for of an electric field to pass through the dielectric material is a given a measurement value known as ε, called the permittivity. The insulator is called the dielectric and is some material that will prevent electric current from passing through it. What makes a capacitor?Ī simple capacitor uses two parallel plates of conductive material separated by an insulator.
The distance of the gap and the material in the gap (air, glass, mineral, liquid, etc.) isn’t too much though to prevent a strong enough electric field to push on electric charges to make them collect on the surfaces. However, it has a gap between the two surfaces that insulates them from each other.

A capacitor is a device that uses two conductive surfaces to store an electric charge.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
